Electrostatics of Conductors
Electrostatics of Conductors: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Charge Distribution for Two Large Parallel Plates, Properties of Conductor, Corona Discharge & Electrostatic Pressure etc.
Important Questions on Electrostatics of Conductors
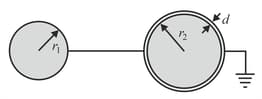
Two metal spheres of radius and , are connected by a thin conducting wire. The second sphere is surrounded by a grounded concentric conducting shell with uniform separation between their facing surfaces. If the second sphere is given a charge , find charges acquired by all the three spheres. Assume that , and the distance between the spheres is much larger than their radii.
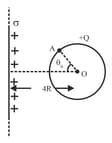
A conducting sphere of radius and charge is placed near a uniformly charged nonconducting infinitely large thin plate having surface charge density . Then find the potential at point (on the surface of sphere) due to charge on sphere (here , )
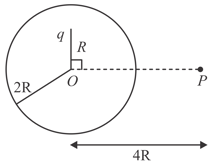
A point charge is kept inside a conducting shell of radius at a distance of from center. Magnitude of field due to induced charges on the inner surface of the shell at point is
Is the electric field inside a cavity (with no charge) zero, even if the shell is not spherical, but has any irregular shape? Explain.
Charge on both surfaces of middle metal plate
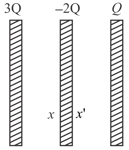
Charges are given to three large parallel conducting plates as shown in figure. Now the switch '' is closed. The value of electric field between the plates (2) and (3) is (each plate has surface of Area A)
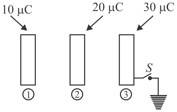
A hollow uncharged spherical conductor has inner radius and outer radius . A positive point charge is in the cavity at the centre of the sphere. Find the potential everywhere, assuming that at ,
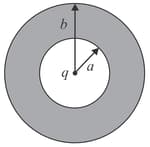
A spherical conducting shell of inner radius and outer radius has a charge .
(a) A charge is placed at the centre of the shell. What is the surface charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell?
(b) Is the electric field inside a cavity (with no charge) zero, even if the shell is not spherical, but has any irregular shape? Explain.
What will be the charges on the sphere after the switch is closed.
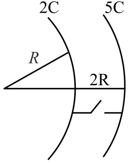
There is a conductor with cavity of radius as shown in figure. A point charge is placed at distance from centre of cavity. A point is at distance from centre of conductor. If the electric field at point is then find
Three identical metallic plates are kept parallel to one another at a separation of and . The outer plates are connected by a thin conducting wire and a charge is placed on the central plate then charge on the inner surface of plate is
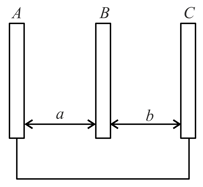
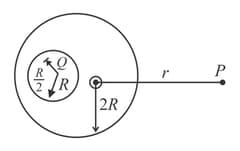
Find the ratio of charges on the inner and outer surfaces of shell , if and charges are given to three concentric conducting spherical shells and respectively as shown in figure.
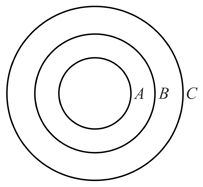
What is the potential of the metallic shell ? If the three concentric metallic shells and , having radii respectively are given surface charge densities respectively. Take .
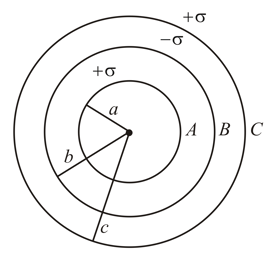
A system consists of three concentric metal shells , and with radii and respectively. Shell is connected to earth and outermost shell is given a charge . Now if shell is connected to shell , then the final charge on the shell is then find the value of .
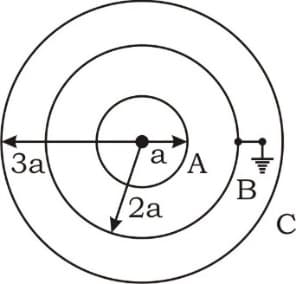
There are three concentric conducting spherical shells. All of them are charged , and radius . The innermost sphere is earthed then find the magnitude of charge transfer from the Earth.
Three concentric metallic spherical shells of radii are given charges respectively. It is found that the surface charge densities on the outer surfaces of the shells are equal. Then, the ratio of the charges given to the shells, , is:-
A charge is distributed over two concentric hollow spheres of radii and such that the surface densities are equal. Find the potential at the common centre.
Can electric field at some point be zero though electric potential is not zero? Give example.
The internal and external pressures for a soap bubble are same. The surface tension of soap solution is and its diameter is . Determine the charge on soap bubble.
Establish expression for maximum charged density for the equilibrium of a charged soap bubble in a vacuum.
